Available online: 09/04/2019
Editorial
REC Interv Cardiol. 2020;2:310-312
The future of interventional cardiology
El futuro de la cardiología intervencionista
Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia, United States
INTRODUCTION
The randomized clinical trial (RCT) has become the gold standard for evaluating clinical treatments thanks to its low selection bias and unknown confounders. However, good clinical practice guidelines and demands from regulatory agencies have become so elaborate over time that, basically, only big pharmaceutical companies have the resources to conduct large RCTs. Therefore, important questions raised by academic scientists could be impossible to test in clinical trials.
One way to circumvent these problems is to use the registry-based randomized clinical trial (RRCT) design. A RRCT uses the platform of an already-existing high-quality observational health registry as a case-report form for randomization and follow-up purposes. This design facilitates the randomization of a large number of patients over a short period of time, reduces costs to a fraction of the cost of conventional randomized clinical trials, and facilitates the follow-up of all eligible patients not enrolled in the study (table 1).1-4
Table 1. Major functions for trial conduction provided by the registry
| Major functions for trial conduction provided by the registry |
| Identification of eligible patients |
| Alert investigator of an eligible patient |
| Link to randomization module |
| Randomization |
| Collection of baseline and procedural characteristics from a registry (eCRF) |
| Presentation of additional trial-specific questions for eCRF |
| Identification of clinical endpoints (endpoint detection) |
| Clinical outcomes reporting |
| Reporting of characteristics of enrolled and non-enrolled patients from the overall population |
|
eCRF, electronic case report form. |
RRCT-SUITABLE REGISTRIES
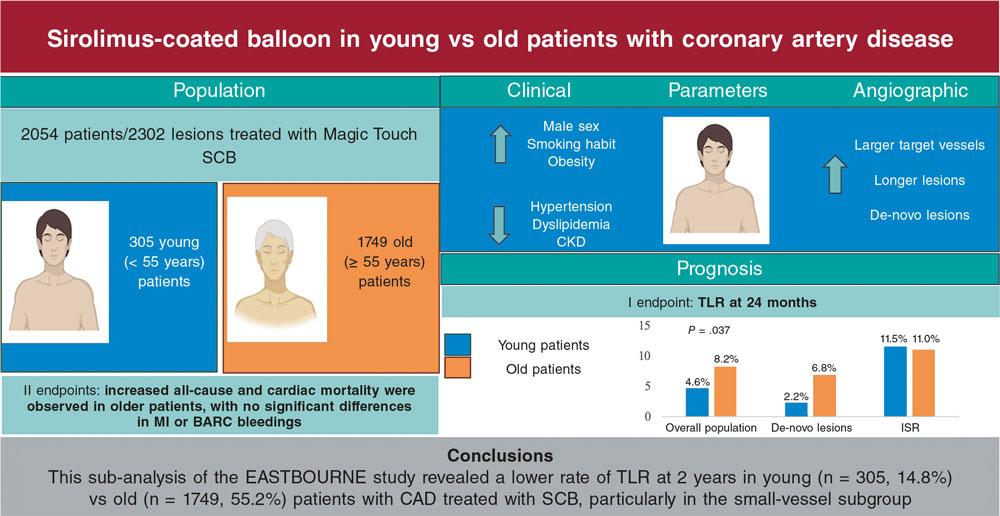
Nearly all healthcare data are stored digitally today, which poses an excellent opportunity to use these data in a RRCT. However, healthcare records are often not structured in a way that allows useful data extraction. Today, disease-specific quality registries with full nationwide coverage are the most suitable ones as the basis for RRCTs, but this may change in the future. Our experience comes from using the Swedish Web-system for the Enhancement and Development of Evidence-based care in Heart disease Evaluated According to Recommended Therapies (SWEDEHEART) and its Swedish Coronary Angiography and Angioplasty Registry (SCAAR)5 through which a large number of RRCTs have been conducted or are in ongoing phases (table 2).6-10 The validation of registry data vs health records has an overall percent agreement of 96%.11 The first pure RRCT was the TASTE trial where thrombus aspiration in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) was studied with mortality as the primary endpoint.1 A large number of patients were rapidly included and with a limited budget by only using registries of baseline demographics, randomization, and endpoint collection in a prospective and randomized fashion. In this trial of a simple device intervention and a solid endpoint, the SWEDEHEART registry provided all the necessary steps to conduct a RCT (table 1). First, identify eligible patients and “flag” them with a pop-up window to the investigator appointed prior to the procedure. Secondly, open up a randomization window with 2 questions: Have the inclusion/exclusion criteria been met? Has the patient given his consent to enter the study? If the answers to both these questions were positive, the patient was randomized and the result shown on the screen momentarily. Thirdly, both the baseline characteristics and the follow-up endpoints were collected from the registry. Furthermore, data on all of the unrecruited patients with complete baseline characteristics are collected. It is interesting to compare the TASTE to the TOTAL trial that examined thrombus aspiration using the traditional RCT design.12 While the cost of the TOTAL trial was approximately €15 000 000 with 87 centers enrolling patients for 48 months on a 6-month follow-up, the cost of the TASTE trial was €500 000 (3%!) with 30 centers enrolling patients for 33 months on a 42-month follow-up being the results nearly identical. In these circumstances of low complexity in both treatment and endpoints an RRCT is superior, in almost every aspect, to a traditional RCT.
Table 2. Registry-based randomized clinical trials in the SWEDEHEART registry: completed, ongoing or in the pipeline
| RRCT | Patients, N | Question | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| TASTE, Fröbert et al.1 (2013) | 7200 | Thrombus aspiration in primary PCI | 2013 + 2014 |
| IFR-SWEDEHEART, Gotberg et al.6 (2017) | 2018 | iFR vs FFR in stable angina or ACS | 2017 |
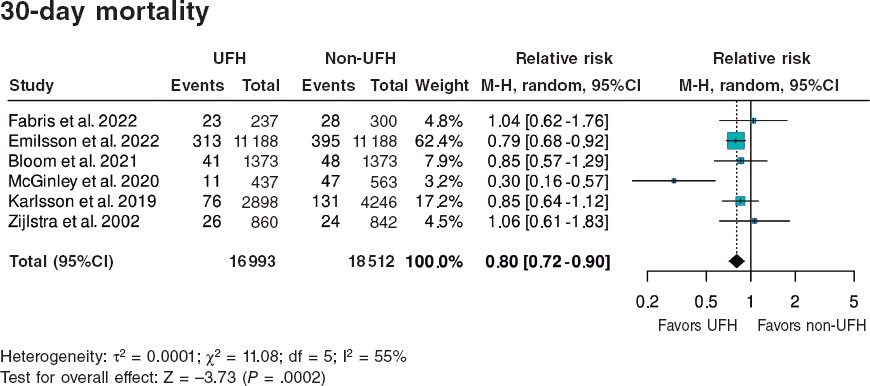
| VALIDATE-SWEDEHEART Erlinge et al.7 (2017) | 6006 | Bivalirudin vs UFH for PCI in ACS | 2017 |
| DETO2X-AMI, Hofmann et al.8 (2017) | 6629 | Oxygen therapy in MI | 2017 |
| FULL-REVASC, NCT02862119 | 4052 | FFR-guidance in MI | Enrollment stopped after 1545 patients |
| PROSPECT-II, NCT02171065 | 900 | Near-infrared spectroscopy in PCI | Presented, TCT 2020 |
| IAMI, Fröbert ret al.9 (2017) | 4400 | Influenza vaccination after MI | Completed enrollment |
| SPIRRIT, NCT02901184 | 3200 | Spironolactone for HFpEF | Ongoing |
| REDUCE, NCT03278509 | 6600 | Beta-blocker post MI in patients with ejection fraction > 50% | Ongoing |
| ABC-AF, NCT03753490 | 6500 | Biomarker score-based treatment vs standard care | Ongoing |
| MINOCA-BAT, NCT03686696 | 2048 | ACEi/beta-blockers after MI with non-obstructive CAD | Ongoing |
| TACSI, NCT03560310 | 2200 | Post-CABG ACS, ticagrelor | Ongoing |
| SWEDEGRAFT, NCT03501303 | 902 | CABG grafting | Completed enrollment |
| Infinity-Swedeheart, NCT04562805 | 2400 | Disengaging DES vs DES | Ongoing |
| DAPA-MI, NCT04564742 | 6400 | SGLT2 inhibitor post-AMI | Ongoing |
| HELP-SWEDEHEARTa | 20 000 | Helicobacter pylori screening after AMI to prevent upper gastrointestinal bleeding (cluster-randomization) | Q2, 2021 |
| SWITCHb | 20 000 | Prasugrel or ticagrelor post-MI (cluster-randomization) | In the pipeline |
| BROKEN-Swedeheart, NCT04666454 | 1000 | Optimal medical treatment for Tako-tsubo syndrome | In the pipeline |
|
a Still unregistered; pilot study: NCT04289012. b Still unregistered. ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; ACS, acute coronary syndromes; CABG, coronary artery bypass graft; CAD, coronary artery disease; DES, drug-eluting stent; FFR, fractional flow reserve; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; iFR, instantaneous wave-free ratio; MI, myocardial infarction; EFPCI cabg SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2; PCI percutaneous coronary intervention; TCT, Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics conference; UFH, unfractionated heparin. |
|||
ADVANTAGES AND LIMITATIONS OF PURE RRCTs COMPARED TO TRADITIONAL RCTs
The major advantages of the RRCT design are: a) a broader and more representative population to clinical reality; in the TASTE and VALIDATE-SWEDEHEART trials 70% of all eligible patients were included1,7; b) clinically significant endpoints were included, and not multiple composite weak or surrogate endpoints; c) long-term follow-up periods, actually life-long follow-ups, if applicable; d) thanks to random selection, bias and confounding factors are reduced to a minimum; e) significantly lower costs; f) rapid inclusion of a large number of patients; and g) initiated and conducted by independent academic researchers with no links to the industry.
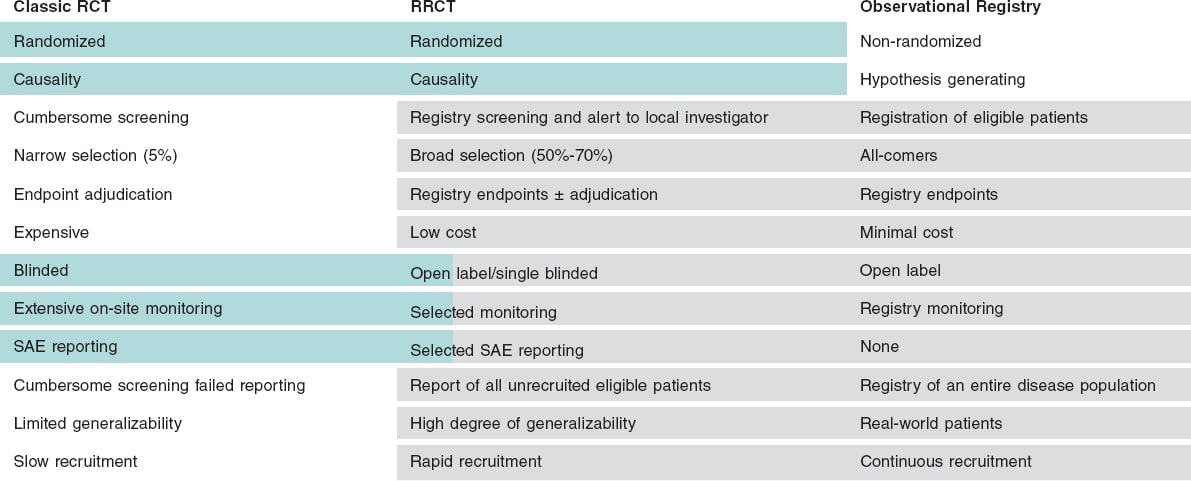
The limitations are: a) open label design with a risk of biased endpoint reporting; b) rare, unexpected events may be missing, and serious adverse event reporting may be difficult; c) events are, for the most part, not adjudicated, which may result in variable data quality; d) difficulties having central chemical analysis and biobanking; e) long-term oral drugs can be difficult to distribute and follow; and f) lack of or limited site monitoring (figure 1).
Figure 1. Comparison of traditional randomized clinical trials (RCTs), registry studies, and registry-based randomized clinical trials (RRCT). Classical RCTs are the gold standard of clinical research, but they have limitations because they are very expensive, selective, and a cumbersome process. Retrospective registry studies can be conducted much cheaper, and may be more representative of the real world, yet they are always hampered by unknown confounders. An RRCT can profit from the best parts of these modalities. SAE, serious adverse event.
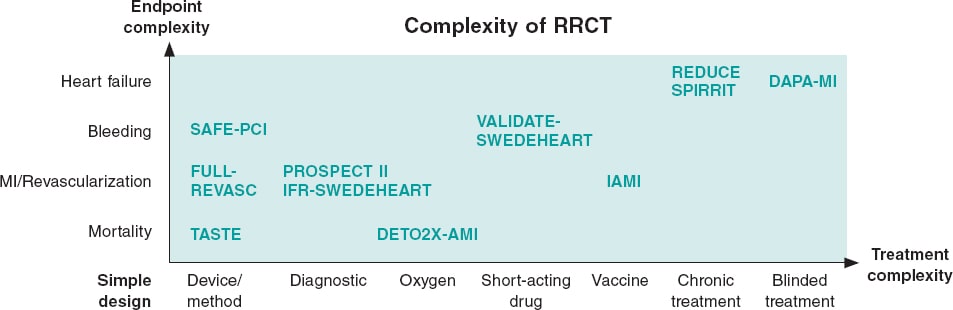
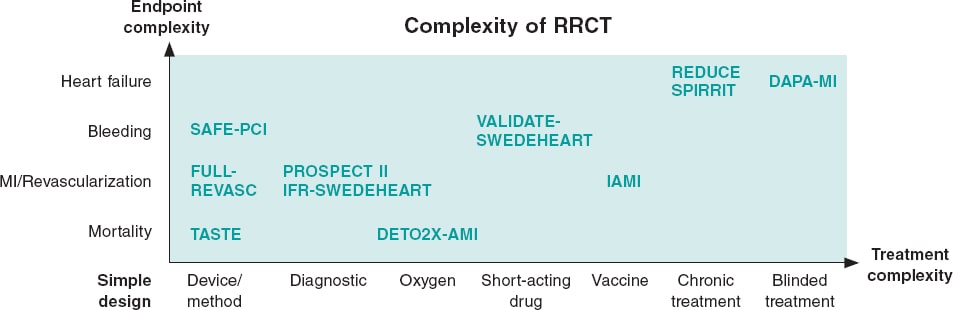
Depending on the limitations of the registry used, need for treatment escalation or endpoint complexity the RRCT can be complemented with different traditional trial elements resulting in a hybrid RRCT (figure 2).
Figure 2. Simple versus complex registry-based randomized clinical trials (RRCT). The purest RRCT examines a simple therapy like a thrombus aspiration device and has a robust endpoint like mortality. When the complexity increases for either treatment or endpoint, then additions to the RRCT design have to be made. These additions could be phone calls, central adjudication, or even blinded treatment with placebo. This increases complexity and costs, but the registry may still be the basis for the trial and facilitate performance. MI, myocardial infarction.
DEVELOPMENT OF RRCTs
In the SORT OUT series of coronary stent trials, baseline demographics and endpoint screening were conducted using a registry approach. However, randomization took place using different approaches (telephone allocation service, internet-based randomization systems), and endpoints were centrally adjudicated.13 In the SAFE-PCI study, randomization was performed outside the registry obtaining additional clinical information and adjudication to the registry data.14
In the VALIDATE-SWEDEHEART trial, 2 short-acting IV antithrombotic agents (bivalirudin and heparin) were assessed using the RRCT approach. As far as we know, this was the first pharmaceutical RRCT ever conducted.7 In a pharmaceutical trial the requirements from the medical regulatory authorities are more demanding even if the drugs have been approved and used for decades. Furthermore, we realized that our registry did not capture bleeding complications satisfactorily. Therefore, we added phone calls after 7 to 180 days followed by the central adjudication of bleeding complications and MI, limited serious event reporting, and data on the entire index hospitalization. Thanks to the simplicity of the trial, 25 centers were able to enroll over 6000 patients with MI over 2 years. Some large centers enrolled more than 1000 patients (figure 2, table 2).
In the IFR-SWEDEHEART trial the instantaneous wave-free ratio diagnostic modality was evaluated. The complexity of the intervention was low, but the composite endpoint included MI and unplanned revascularization.6 Although the endpoints were found in the registries, data were collected from medical records from the centers and adjudicated by a central committee.
In the DETO2X-AMI trial the endpoint was mortality, which does not need adjudication; however, the oxygen of the procedure had to be administered to the patient in a single blinded fashion adding some extra complexity to the study8 (figure 2, table 2). Similarly, the influenza vaccine study conducted post-MI (IAMI trial) needed blinded treatment.9 Furthermore, other countries without the SWEDEHEART registry structure were needed to get a sufficient number of patients, which resulted in a parallel randomization module and electronic case report forms (figure 2, table 2).9
There are 2 ongoing RRCTs with chronic oral treatment and a composite endpoint of death and hospitalizations due to heart failure: the REDUCE (beta-blocker post-MI, NCT03278509) and the SPIRRIT (Spironolactone for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction, NCT02901184). However, despite the complex treatment and endpoint of both of them, they rely nearly only on registries. The treatment is randomized in the registry, prescribed, and then followed by the Swedish Prescribed Drug Register. Hospitalizations due to heart failure are collected from the National Patient Register where this diagnosis has proven to have a high validity in previous studies.
FUTURE POSSIBILITIES OF THE RRCT CONCEPT
So far, the RRCT technology has mostly been used for the assessment of devices or generic drugs that have been used for decades often with results that the treatment examined has been redundant, as it has been the case with the TASTE and VALIDATE-SWEDEHEART trials. Sometimes, as it occurred with the IFR-SWEDEHEART study, a new diagnostic procedure proves to be non-inferior to the current standard.6 This resulted in an IA recommendation for the instantaneous wave-free ratio in the clinical practice guidelines. In general, RRCTs have been deemed unsuitable by the medical regulatory authorities for first approval, but this is about to change. The INFINITY trial (NCT04562805) is examining a new type of stent capable of disengaging its metal struts after half a year. This is a currently ongoing RRCT whose objective is to support an approval given by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Demographics, randomization, and endpoint follow-up are already taken care of by the SWEDEHEART registry, still a phone call at 1 month and 1 year combined with central adjudication was added.
The first study, that has been analyzing an expanded use for an oral drug, is the DAPA-MI study (NCT04564742) where dapagliflozin is being tested for post-MI patients with reduced ejection fraction but without diabetes. The registry is the basis of the study, yet visits have been added to dispense the blinded medication. The study is sponsored by AstraZeneca and intends to develop new more cost-efficient ways to conduct phase III trials. The study profits from 2 countries with nationwide MI registries, the UK and Sweden, with their MINAP16 and SWEDEHEART5 registries, respectively.
In Europe, the European Society of Cardiology has mostly relied on surveys to register different heart conditions. These are valuable, but they only give us a snapshot of a short timeframe and the selection of patients is unclear and may not be representative of the real world. However, a new initiative called EuroHeart17 has been trying to establish a common basic structure for continuous cardiac registries that could be used by any countries. One of its objectives is to facilitate conducting RRCTs in several European countries making the results more representative and allowing larger studies being conducted more rapidly.
CLUSTER-RANDOMIZED RRCTs
Cluster randomization design simplifies enrollment and does not often require signed informed consent forms, only general information about the ongoing study. It facilitates the recruitment of nearly all patients from a region during a certain period of time and it basicaly uses a cross-over design. In the HELP-SWEDEHEART trial—still not registered—20 000 patients diagnosed with MI in the SWEDEHEART registry will, based on hospital data, be cluster-randomized in a crossover design to receive Helicobacter pylori screening and, if they test positive, be recommended eradication therapy. The primary endpoint is upper gastrointestinal bleeding, which is collected from the National Patient Register. The still unregistered SWITCH trial is planning to investigate prasugrel compared to ticagrelor for the treatment of patients hospitalized due to MI with the composite endpoint of death, MI or stroke collected from the National Patient Register and the National Cause of Death Registry. A total of 4 Swedish regions will be randomized in blocks to standard use of either prasugrel or ticagrelor over 2 years.
In conclusion, RRCTs combine some of the best parts of the classical RCT design and traditional registries when conducting large, randomized, real-world, representative, and cost-effective clinical studies. They give academic researchers an opportunity to obtain important clinical answers that would have never been funded by industry.
FUNDING
The study is supported by the Swedish Heart and Lung Foundation, the Swedish Scientific Research Council, and the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation. The author is solely responsible for the content of this manuscript.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
D. Erlinge declares having received speaker or advisory board fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Sanofi, and Chiesi.
REFERENCES
1. Fröbert O, Lagerqvist B, Olivecrona GK, et al. Thrombus aspiration during ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1587-1597.
2. James S, Frobert O, Lagerqvist B. Cardiovascular registries:a novel platform for randomised clinical trials. Heart. 2012;98:1329-1331.
3. Yndigegn T, Hofmann R, Jernberg T, Gale CP. Registry-based randomised clinical trial:efficient evaluation of generic pharmacotherapies in the contemporary era. Heart. 2018;104:1562-1567.
4. Lauer MS, D'Agostino RB, Sr. The randomized registry trial--the next disruptive technology in clinical research?N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1579-1581.
5. Start - SWEDEHEART (uu.se). Available at: https://www.ucr.uu.se/swedeheart/start-scaar. Accessed 8 Feb 2021.
6. Gotberg M, Christiansen EH, Gudmundsdottir IJ, et al. Instantaneous Wave-free Ratio versus Fractional Flow Reserve to Guide PCI. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1813-1823.
7. Erlinge D, Omerovic E, Frobert O, et al. Bivalirudin versus Heparin Monotherapy in Myocardial Infarction. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1132-1142.
8. Hofmann R, James SK, Jernberg T, et al. Oxygen Therapy in Suspected Acute Myocardial Infarction. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1240-1249.
9. Fröbert O, Gotberg M, Angeras O, et al. Design and rationale for the Influenza vaccination After Myocardial Infarction (IAMI) trial. A registry-based randomized clinical trial. Am Heart J. 2017;189:94-102.
10. Hambraeus K, Held C, Johansson P, et al. SWEDEHEART Annual report 2012. Scan Cardiovasc J. 2014;48(Suppl 63):2-133.
11. Jernberg T, Attebring MF, Hambraeus K, et al. The Swedish Web-system for enhancement and development of evidence-based care in heart disease evaluated according to recommended therapies (SWEDEHEART). Heart. 2010;96:1617-1621.
12. Jolly SS, Cairns JA, Dzavik V. Primary PCI with or without Thrombectomy. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:682-683.
13. Raungaard B, Jensen LO, Tilsted HH, et al. Zotarolimus-eluting durable-polymer-coated stent versus a biolimus-eluting biodegradable-polymer-coated stent in unselected patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (SORT OUT VI):a randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2015;385:1527-1535.
14. Rao SV, Hess CN, Barham B, et al. A registry-based randomized trial comparing radial and femoral approaches in women undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention:the SAFE-PCI for Women (Study of Access Site for Enhancement of PCI for Women) trial. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7:857-867.
15. Neumann FJ, Sousa-Uva M, Ahlsson A, et al.;ESC Scientific Document Group. 2018 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization. Eur Heart J. 2019;40:87-165.
16. NICOR. Myocardial Ischaemia/MINAP (Heart Attack audit). Available at: https://www.nicor.org.uk/national-cardiac-audit-programme/heart-attack-audit-minap/. Accessed 8 Feb 2021.
17. European Society of Cardiology. EuroHeart. Available at: https://www.escardio.org/Research/euroheart. Accessed 8 Feb 2021.
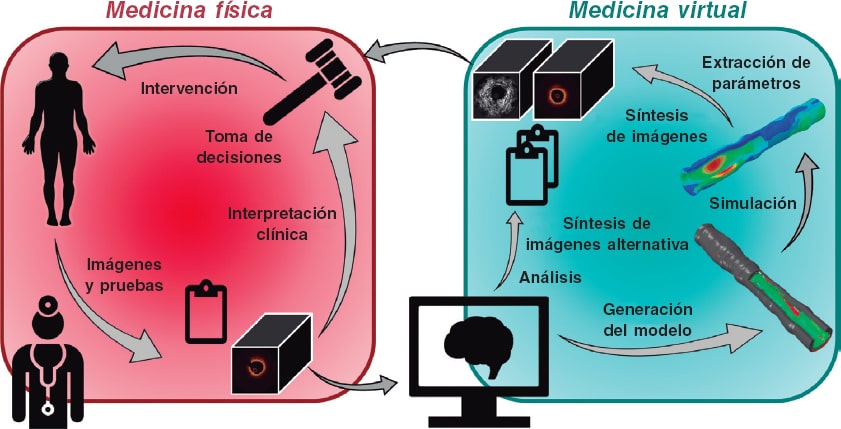
Medicine and technology have long advanced hand-in-hand. Clinicians push boundaries, expertly yielding the tools at their disposal. Scientists and engineers, in turn, respond to the demands and needs of clinicians by developing the next generation of tools, thereby expanding the space in which clinicians can operate and explore. This boundary-pushing partnership is particularly prevalent in the field of interventional cardiology, which has enthusiastically and effectively embraced advancements in percutaneous and imaging technologies to revolutionize cardiovascular medicine. Continuing this tradition, several developments in computational processing and modeling promise to enhance the utility and efficacy of arterial imaging, with some tools having already entered the clinical setting. For example, a tool that uses computational models built from computed tomography angiography to assess the fractional flow reserve has improved the clinical decision-making process and lowered the rates of unnecessary invasive procedures.1 Additional tools will further unify the physical and virtual realms of medicine through the bridge provided by imaging, offering both simple tools to label and quantify individual images and advanced tools to simulate and profile entire lesions. The future of the cooperative alliance between medicine and technology must be continuously nurtured and will continue to thrive with the enthusiastic and critical contributions of well-informed interventional cardiologists.
WHAT IS COMPUTATIONAL PROCESSING AND MODELING?
Computational processing is the application of algorithms and software to perform specified and encoded procedures. Computational processing can be applied to intravascular images to enhance, characterize or detect and quantify features depicted in the images. One application of such processing is to extract physiological features used to generate computational models of the imaged vessel region. Computational modeling is the creation and use of virtual representations of physical systems. Such representations can be programmed with sets of rules that prescribe how they should behave and respond under different conditions, and in that way the models can be used to simulate the behavior of the physical system under various hypothetical scenarios.
Unmet NEEDs IN INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGY
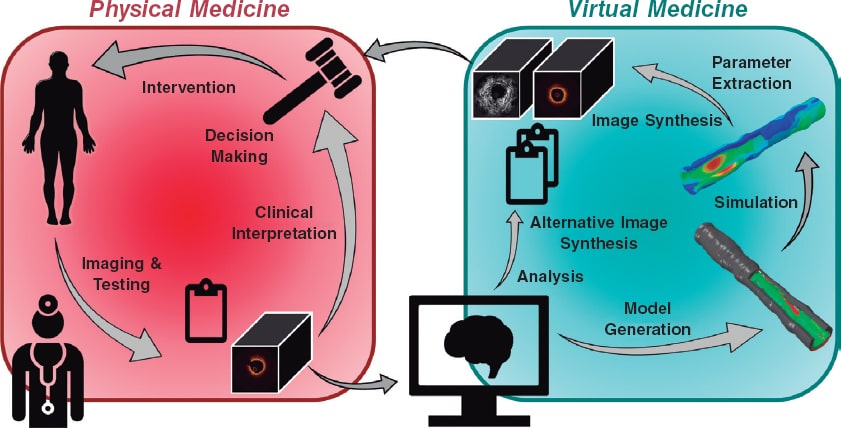
In moving towards a more personalized and precise provision of medical care, the convergence of intravascular imaging with computational processing and modeling will be a pivotal step to empower interventional cardiologists. The role and need for this convergence (figure 1), part of a wider vision of computational cardiology,2 is highlighted by several key challenges faced by the current interventional cardiology practice.
Figure 1. Our vision for the future of cardiovascular medicine is one in which physical and virtual medicine forms a continuum. Clinicians collect data including images and other test results from a patient. Anatomical and morphological information will be automatically extracted by algorithmic processing routines, distilled into reported quantitative metrics, and used to generate patient-specific computational models. Various simulated tests and procedures will be performed on the virtual patient. Results of the analyses and simulations will be transformed back into clinical data to enable a seamless integration and assessment by the heart team; the outcomes could inform the decision-making process and guide the patient's procedure.
Standard assessments with less interventional workload
Among the most critical and urgent roles of computational processing is integrating and augmenting—not displacing—the role played by interventional cardiologists. Computational methods can remove the inter- and intra-observer variability, time consumption, and monotony associated with extensive manual measurements of intravascular images. Such analysis can be performed in the background and continuously without the constraints of busy clinical schedules. Support from processing technologies can also assist physicians with limited training, experience or expertise who may otherwise be unable to identify important features in intravascular images. Additionally, modeling offers relevant quantitative metrics of the vascular state that simply cannot be directly measured, such as estimates of stress along and within the vessel walls.
Patient profiling and stratification
The core premise of precision medicine is that patient populations can be segmented into narrow classes that respond differently to interventions. The cardiology community has proposed broad classifications to divide atherosclerotic plaques, typically driven by the prevailing tissue type and presumed degree of progression.3 Despite or in deference to its simplicity, there have been few significant updates to this classification in recent decades, even as intravascular imaging offers more and richer information on lesion geometry and morphology and as treatment of the disease has evolved. Computational processing and modeling may offer improved profiling of individual patients on the basis of clinical presentation, disease state, detailed lesion phenotype, and even mechanical condition. By computing series of quantitative measures to describe patient and lesion, the possibility of building a more robust patient profile becomes real. Such granular profiling could enable stratification to better assess who benefits the most from which interventions, thus guiding the therapeutic decisions.4
Prediction and risk assessments for clinical decision support
In addition to improved patient profiling and stratification, modeling offers the ability to engage in truly personalized risk assessment and prediction of disease progression under various treatment regimens. Because much of the interpretation of intravascular images is currently qualitative, decision-making during patient care can be an exquisite art and formulaic science alike and depend on each cardiologist’s personal experiences (and biases), training, and institutional practices. Advancing beyond personal clinician experience and intuition, computer processing and modeling offer repeatable, standardized quantification to inform the decision-making process. For example, simulations of detailed patient- and lesion-specific models, or “Digital Twins”,5 could facilitate various virtual interventions or intervention parameters to be tested before selecting an optimal strategy to minimize risk. Alternatively, disease progression and plaque growth models may help to predict which vessels and mild lesions may progress dangerously—suggesting the need for prophylactic action—and which are likely to remain benign and inconsequential over time.
TECHNOLOGICAL Tools in DEVELOPMENT
To fulfill the needs of computational processing and modeling in interventional cardiology, various new technologies are being developed that leverage the rich data available from intravascular imaging. The detection and measurement of geometric features is already available in limited cases, and it is likely to expand. The automated delineation of the lumen and external elastic lamina is incorporated in some intravascular ultrasound systems, and developments in computational processing have recently yielded promising results to identify these, as well as the internal elastic lamina, in optical coherence tomography images. Facilitated by automated detection of inner and outer vessel borders, automatic measurements from pullbacks such as lumen area, plaque burden, eccentricity, and remodeling index will reduce the need for manual identification and annotation of the most critical frames and will enable better visualization of diseased vessels. This information may also be used, for example, in the proper sizing of balloons and stents.
Advances in image processing also offer improved availability of information on lesion morphology. While experts are generally adept at determining the composition and distribution of plaque from cross-sectional images, doing so is a slow process that requires extensive expertise. Increased availability of automated virtual histology will improve the characterization, profiling, and stratification of lesion phenotypes. New image-based methods to characterize the stiffness of diseased tissue also promise greater insight into the mechanical profile of a lesion. Altogether, this information on plaque distribution and properties will help cardiologists to plan and guide interventions (eg, by informing the need for lesion preparation or modification prior to ballooning or stenting).
Computational modeling is a central focus of ongoing technological research and development. The ability to simulate disease progression and interventions is an enticing challenge that has been drawing the attention of multidisciplinary teams. Among these efforts, major collaborative, international European projects have sought to develop and refine advanced predictive models of atherosclerotic plaque processes and angioplasty by integrating patient risk factors, blood panel results, and imaging data.6 Robust longitudinal validation of such models remains an obstacle.
Computational processing offers another little-explored function to synthesize and enhance images. As intravascular imaging is the cornerstone of interventional cardiology, these generative abilities could be used with great effect to improve diagnostic image quality and efficacy, convey information generated from computational models, and facilitate education and training for reading and interpreting images.
Several technologies in development may require changes to future clinical practice. For example, some methods require multiple image pullbacks or simultaneous measurement of pressure and matched image acquisition. Changes will be limited by the corresponding progress in hardware development and adoption, demonstrated cost-benefit tradeoffs for patients, and receptiveness of the interventional cardiology field.
THE Indispensible ROLE OF INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGISTS
Interventional cardiologists will not only have a pivotal role in the future adoption of computational processing and modeling technologies but also an important present role in defining and achieving that future. Those experienced in managing and treating patients are needed to direct, develop, and shepherd new technologies—their deep knowledge of the demands and practical limitations of clinical care are indispensable to scientists and engineers. There is also ongoing profound need for data with which to train and validate new methods and models. Here, too, the involvement, expertise, and contributions of collaborative cardiologists are essential.
The increasing integration of more complex technologies also introduces a growing imperative for cardiologists to further cultivate their technical literacy. While medical and health sciences must remain a priority in the training of interventional cardiologists, broader training is an important prerequisite to critically assess new claims and make informed decisions on the applicability and reliability of new techniques as they enter the medical arena. Clinicians will need to understand the assumptions, uncertainties, and conditions under which these tools should be beneficially applied to treat their patients. Interventional cardiologists and other medical professionals are already well-equipped for many of these tasks. Looking beyond the novelty and flair of the methods, familiar and fundamental concepts considered for other diagnostic tests, such as sensitivity and specificity, should be equally applied to scrutinize advanced new software tools.
As computational processing and modeling converge with intravascular imaging in the coming years, interventional cardiologists will be empowered to deliver more personalized and precise medical care. Those in the field should expect to play an active role in the development, assessment, and adoption of new technologies, and equip themselves with the evolving knowledge and skills necessary to make the most of these tools in the management of their patients.
FUNDING
This work was supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, MD, United States; grant number 5R01GM049039-24) and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (Cambridge, MA, United States; MathWorks Engineering Fellowship).
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
M. Olender and E.R. Edelman have the patent “Arterial Wall Characterization in Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging” (16/415,430) pending, and the patent “Systems and Methods for Utilizing Synthetic Medical Images Generated Using a Neural Network” (62/962,641) pending. In addition M. Olender reports grants from MathWorks while conducting the study; and E.R. Edelman reports grants from the U.S. National Institutes of Health while conducting the study; grants from Abiomed, grants from Edwards LifeSciences, grants from Boston Scientific, grants from Medtronic, grants from Autus Medical, other from Biodevek, other from Panther Therapeutics, personal fees from Abbvie, outside the submitted work.
REFERENCES
1. Douglas PS, Pontone G, Hlatky MA, et al. Clinical outcomes of fractional flow reserve by computed tomographic angiography-guided diagnostic strategies vs. usual care in patients with suspected coronary artery disease:The prospective longitudinal trial of FFRCT:Outcome and resource impacts stud. Eur Heart J. 2015;36:3359-3367.
2. Athanasiou LS, Nezami FR, Edelman ER. Computational Cardiology. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2019;23:4-11.
3. Stary HC, Chandler AB, Dinsmore RE, et al. A Definition of Advanced Types of Atherosclerotic Lesions and a Histological Classification of Atherosclerosis. Circulation. 1995;92:1355-1374.
4. Gray RA, Pathmanathan P. Patient-Specific Cardiovascular Computational Modeling:Diversity of Personalization and Challenges. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2018;11:80-88.
5. Corral-Acero J, Margara F, Marciniak M, et al. The 'Digital Twin'to enable the vision of precision cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:4556-4564.
6. Sakellarios AI, Pelosi G, Fotiadis DI, et al. Predictive Models of Coronary Artery Disease Based on Computational Modeling:The SMARTool System. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2019;2019:7002-7005.
Over the last few years, left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) has gained traction in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation as an alternative to oral anticoagulation to prevent cerebral infarction, especially in patients with some sort of contraindication to these drugs.1
In an article published in REC: Interventional Cardiology, Ruiz-Salmerón et al.2 describe their experience using this technique during the last 10 years. This publication gives us the opportunity to review the cumulative scientific evidence available in this regard that has justified its exponential growth.
In the last national registry published in the United States, the number of physicians and hospitals that perform this intervention has gone from 30 to over 1200 and from 20 to over 400, respectively, within the last 2 years.3 In Spain, according to the registry published by the Interventional Cardiology Association of the Spanish Society of Cardiology, the number of procedures performed within the last 4 years has tripled.4
Left atrial appendage isolation started as a surgical technique back in the 1950s,5 but it was not until the beginning of 2000 when the development of percutaneous interventional procedures finally put this technique on the map.6 However, the turning point was 2009 with the publication of the multicenter and randomized PROTECT AF clinical trial7 that compared the LAAO in over 450 patients implanted with the Watchman device (Boston Scientific, United States) vs conventional treatment with warfarin. It proved the non-inferiority of the intervention for the primary composite of stroke, cardiovascular death or systemic embolism.5 Five years later, the PREVAIL trial8, with a similar design to the PROTECT AF, achieved similar results regarding efficacy, but with success rates over 95% and significantly less common complications (1.9%).
The mid-term follow-up results are even more interesting. At the 3.8-year follow-up, the patients of the PROTECT AF9 experienced a significant benefit in the composite primary endpoint (8.4% vs 13.9%; hazard ratio = 0.61; 95% confidence interval, 0.38-0.97; P = .04) compared to the control group with warfarin. Actually, even all-cause mortality improved in the LAAO group (12.3% vs 18%; hazard ratio = 0.66; 95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.98; P = .04).
Also, the third large randomized clinical trial, the PRAGUE-17,10 that compared LAAO with direct-acting oral anticoagulants in 400 patients, proved the non-inferiority of this procedure compared to new anticoagulants to prevent cardiovascular, neurological or hemorrhagic events associated with atrial fibrillation.
A meta-analysis of these randomized clinical trials proved that LAAO has similar cerebral infarction rates to those of oral anticoagulation (warfarin or new anticoagulants) with significant reductions of cerebral hemorrhages and cardiac and non-cardiac death.11
Added to this, large scale multicenter registries have proven the efficacy and safety of this intervention in patients with contraindications to oral anticoagulation. The EWOLUTION registry of 1021 patients reported a 62% rate of contraindication to oral anticoagulation, a 98.5% success rate, and a 2.7% rate of complications.12 At the 2-year follow-up, cerebral infarction rates of 1.3/100 patients-year (a 83% reduction compared to the historic series) and hemorrhage rates of 2.7/100 patients-year (a 46% reduction compared to the historic series) were reported.13 In line with this, the multicenter registry of the Amulet device (Abbott, United States) that included 1088 patients of whom 83% had contraindications to oral anticoagulation revealed a 99% success rate and a 3.2% rate of complications.14 These results are consistent with almost all the studies published over the last decade.
In our setting we have registries like the one published in this issue of REC: Interventional Cardiology, where Ruiz-Salmerón et al.2 analyze 260 consecutive cases of LAAO in a population of high embolic (CHA2DS2-VASc of 4.3 ± 1.6) and hemorrhagic risk (HAS-BLED of 3.7 ± 1.2). They confirmed a 75.5% reduction of embolic risk and a 58.5% reduction of hemorrhagic risk with respect to the risk predicted by both scales. Also, patients with longer follow-up periods (> 4 years in this case) showed a progressive benefit derived from the intervention (rate of events per 100 patients-year: 0.7 vs 2.0, P = .17 for embolisms; and 1.7 vs 4.0, P = .09 for major hemorrhages) compared to those with shorter follow-up periods.
Studies like this are necessary since we don’t have too many studies on long-term experiences with LAAO with mean follow-up periods > 2.5 years. It is only from this long-term follow-up perspective that we will be able to understand the impact of an intervention largely, based on the prophylaxis of the thromboembolic complications that may occur during a patient’s lifetime.
Finally, we should mention that scientific societies like the European Heart Rhythm Association and the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions15 support the benefits of LAAO in situations of contraindication to oral anticoagulation, high risk of bleeding, cerebral infarction under anticoagulation or even in patients who, after being properly informed, reject oral anticoagulation. However, the current clinical practice guidelines published by the European Society of Cardiology1 still assign a low level of recommendation (IIb-B) for patients with atrial fibrillation contraindicated to long-term courses with oral anticoagulants (eg, patients with intracranial hemorrhages without reversible cause). In any case, the results of 2 ongoing large scale randomized clinical trials of LAAO vs direct-acting oral anticoagulants, the CHAMPION-AF (NCT04394546) and the CATALYST (NCT04226547) will conclusively establish the level of recommendation of this technique in patients without contraindications to oral anticoagulation.
In conclusion, we should assert that the LAAO is an effective and safe technique. With the cumulative data obtained over the last decade, its utility is undeniable in patients with atrial fibrillation who cannot take oral anticoagulation to prevent the occurrence of strokes. Also, clinical trials have proven its advantages vs warfarin, and even the long-term follow-up of these patients has offered significant positive results, even reducing mortality rate compared to oral anticoagulation. The results of the new clinical trials vs direct-acting oral anticoagulants will determine the large-scale future of this procedure.
FUNDING
I. Cruz-González has received research grants from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (PI19/00658) and the regional health management of the Board of Castille and León (GRS 3031/A/19).
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
I. Cruz-González is a proctor for Boston Scientific, Lifetech and Abbott, and a consultant for IHT and Qatnamedical. D. González-Calle declared no conflicts of interest whatsoever.
REFERENCES
1. Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur Heart J. 2021;42:373-498.
2. Ruiz-Salmerón RJ, Ronquillo-Japón M, Carlos Robles-Pérez, et al. Una década de cierre percutáneo de la orejuela izquierda:desde el procedimiento hasta el beneficio a largo plazo. REC Interv Cardiol. 2021;3:112-118.
3. Freeman JV, Varosy P, Price MJ, et al. The NCDR Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Registry. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:1503-1518.
4. Ojeda S, Romaguera R, Cruz-González I, Moreno R. Spanish Cardiac Catheterization and Coronary Intervention Registry. 29th Official Report of the Interventional Cardiology Association of the Spanish Society of Cardiology (1990-2019). Rev Esp Cardiol. 2020;12:927-936.
5. Madden JL. Resection of the left auricular appendix;a prophylaxis for recurrent. J Am Med Assoc. 1949;140:769-772.
6. Sievert H, Lesh MD, Trepels T, et al. Percutaneous left atrial appendage transcatheter occlusion to prevent stroke in high-risk patients with atrial fibrillation:Early clinical experience. Circulation. 2002;105:1887-1889.
7. Holmes DR, Reddy VY, Turi ZG, et al. Percutaneous closure of the left atrial appendage versus warfarin therapy for prevention of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation:a randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2009;374:534-542.
8. Holmes DR, Kar S, Price MJ, et al. Prospective randomized evaluation of the watchman left atrial appendage closure device in patients with atrial fibrillation versus long-term warfarin therapy:The PREVAIL trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:1-12.
9. Reddy VY, Sievert H, Halperin J, et al. Percutaneous left atrial appendage closure vs warfarin for atrial fibrillation:a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2014;312:1988-1998.
10. Osmancik P, Herman D, Neuzil P, et al. Left Atrial Appendage Closure Versus Direct Oral Anticoagulants in High-Risk Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3122-3135.
11. Turagam MK, Osmancik P, Neuzil P, Dukkipati SR, Reddy VY. Left Atrial Appendage Closure Versus Oral Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:2795-2797.
12. Boersma LVA, Schmidt B, Betts TR, et al. Implant success and safety of left atrial appendage closure with the WATCHMAN device:peri-procedural outcomes from the EWOLUTION registry. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2465-2474.
13. Boersma LV, Ince H, Kische S, et al. Evaluating Real-World Clinical Outcomes in Atrial Fibrillation Patients Receiving the WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Technology:Final 2-Year Outcome Data of the EWOLUTION Trial Focusing on History of Stroke and Hemorrhage. Circ Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2019;12:e006841.
14. Landmesser U, Schmidt B, Nielsen-Kudsk JE, et al. Left atrial appendage occlusion with the AMPLATZER Amulet device:Periprocedural and early clinical/echocardiographic data from a global prospective observational study. EuroIntervention. 2017;13:867-876.
15. Glikson M, Wolff R, Hindricks G, et al. EHRA/EAPCI expert consensus statement on catheter-based left atrial appendage occlusion —an update. EuroIntervention. 2020;15:1133-1180.
The management of symptomatic severe aortic stenosis is based on surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) or transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI).
In an interesting work recently published on REC: Interventional Cardiology, Núñez-Gil et al.1 studied how the type of hospital and volume of cases impacted the results obtained with both techniques. This was a retrospective analysis with data gathered from administrative sources with the limitations associated with studies based on the Minimum Basic Dataset. Nonetheless, it leaves important messages that should be discussed.
In line with other publications,2 they describe the correlation between casuistry, case volume, and results in terms of mortality and risk-adjusted hospital stays. This article is original and important because in Spain, no study like this has ever been conducted on the association between the volume of TAVIs performed and results.
Also, they confirm the existence of a favorable correlation between better TAVI results and in-hospital «structural» variables like the availability of cardiac surgery intensive care units (CICU). The authors stress the importance behind the finding that there is a correlation between the presence of a CICU and a lower mortality rate with both techniques. However, this impact is greater with TAVI compared to SAVR. Actually, having defined protocols and staff trained in the rapid detection and management of periprocedural complications like vascular access hemorrhages, atrioventricular blocks, renal failure, etc. would explain this correlation.
Data from this study show that the risk-adjusted in-hospital mortality rate is lower in large volume centers and high-level hospitals («type 4»). It is logical to think that large volume PCI-capable centers with all their resources and wide experience in coronary and structural heart procedures will have good results. Performing a high number of procedures reduces procedural complications. However, achieving a solid learning curve first is essential to have good clinical results and increase the cost-effectiveness of the procedures. However, nowadays, the learning curve is shorter with the new devices available.
On the other hand, they found that large volume centers that perform TAVIs and also quite a few SAVRs have a lower mortality rate with percutaneous procedures. The large casuistry with both procedures and the extensive experience of interventional cardiologists and surgeons improves the results. This may be explained by the benefits derived from the mutual collaboration between interventional cardiologists and surgeons regarding the selection of the most appropriate cases for each technique or because surgeons who perform more surgeries have a greater expertise to solve eventual TAVI complications. Still, the need for surgery today is very low.3,4 It may also be suggested that these hospitals have a greater surgical activity because they receive a large number of patients with severe aortic stenosis (some treated with SAVR and others with TAVI).
Hospitals that perform large volumes of TAVIs but very few surgeries also have good results. Therefore, it does not seem to be a factor directly associated with surgical activity per se, but rather with the experience of interventional cardiologists and the writing of proper protocols before, during, and after the procedure.
Consistent with all this, the authors also say that the availability of a CICU is important in the results of TAVI because it guarantees proper treatment after the procedure.
The importance of this article is undeniable, and its findings are very interesting. However, its conclusions should be interpreted with caution. On the one hand, there is too much heterogeneity among the hospitals studied. On the other hand, there may be biases and factors that still remain unstudied. Some of the possible biases may be that patients treated with TAVI in type 3 hospitals without CICU capabilities may have higher comorbidity rates. Also, there are variables not included in the study that may impact the results like the analysis of the valves used or the timeframe of the process analyzed in each hospital, which could also impact the results differently depending on the timing of the learning curve.
The correlation between volume and results has already been proven in other studies.5 However, it seems to decrease in time with more experience, better hospital processes, and more advanced technologies.
Also, there are important additional questions that should be taken into consideration like the analysis of other complications that were not included in the study (eg, need for pacemaker, onset of renal failure, etc.).
Over 4000 annual TAVIs are performed in Spain every year in nearly 110 hospitals by interventional cardiologists who, in collaboration with clinical cardiologists, imaging specialists, and other health professionals—geriatrician, anesthesiologists, intensivists, surgeons, radiologists—achieve excellent results that have been improving throughout the years.
As a consequence of these and other data published, TAVIs should only be performed after proper training, in large enough numbers, and with good results.6,7
In conclusion, the article of Núñez-Gil et al.1 is an interesting study that shows the commitment of interventional cardiologists to optimize the results of TAVI. A commitment that is already a reality in many Spanish cath labs.
FUNDING
No funding was received for this work.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
None reported.
REFERENCES
1. Núñez-Gil IJ, Elola J, García-Márquez M, et al. Reemplazo valvular aórtico percutáneo y quirúrgico. Influencia del volumen y del tipo de centro tratante en los resultados. REC Interv Cardiol. 2021;3:103-111.
2. Kaier K, Oettinger V, Reinecke H, et al. Volume–outcome relationship in transcatheter aortic valve implantations in Germany 2008–2014:a secondary data analysis of electronic health records. BMJ Open. 2018;8:e020204.
3. Cid A, Rodríguez Leor O, Moreno R, Pérez de Prado A. Registro Español de Hemodinámica y Cardiología Intervencionista. XXVIII Informe Oficial de la Sección de Hemodinámica y Cardiología Intervencionista de la Sociedad Española de Cardiología (1990-2018). Rev Esp Cardiol. 2019;72:1043-1053.
4. Jiménez-Quevedo P, Muñoz-García A, Trillo-Nouche R, et al. Evolución temporal en el tratamiento transcatéter de la estenosis aórtica:análisis del registro español de TAVI. REC Interv Cardiol. 2020;2:98-105.
5. Arora S, Strassle PD, Qamar A, et al. Trends in inpatient complications after transcatheter and surgical aortic valve replacement in the transcatheter aortic valve replacement era. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;11:e007517.
6. Eggebrecht H, Mehta RH, Haude M, et al. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) by centres with and without an on-site cardiac surgery programme:preliminary experience from the German TAVI registry. EuroIntervention. 2014;10:602-608.
7. Tamburino CI, Barbanti M, Tamburino C. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation:how to decrease post-operative complications. Eur Heart J Suppl. 2020;22(Suppl E):E148-E152.

WHAT DO WE KNOW ABOUT FRACTIONAL FLOW RESERVE AFTER STENTING?
The introduction of the concept of fractional flow reserve (FFR) in the mid 90s moved coronary physiology from experimental science to routine use at the cath lab.1-3 Added to the better understanding of basic physiological mechanisms such as self-regulation and compensatory vasodilation and the coronary flow reserve introduced 20 years earlier by Gould et al.,4 FFR has undeniably changed our interpretation of coronary angiograms and had a major influence on the clinical decision-making process, and patient outcomes.3,5,6 This has resulted in the unique adoption of FFR as the only physiological index with a class I A indication for use in the clinical practice guidelines produced by the most important cardiologic societies worldwide.7,8
FFR has taught us that coronary angiography and the anatomic images we can acquire at the cath lab only provide moderately reliable measures of the functional significance of coronary artery disease and myocardial ischemia. Also, there is undeniable proof that the decision-making process based on functional measurements leads to better outcomes compared to angiography alone.3,5,6
In contrast, the interpretation of FFR after coronary intervention is still ambiguous. Basically, we should be aware that the status of a coronary artery immediately after a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) changes and is prone to much more variability compared to a situation of chronic stable coronary artery disease. An excellent result of a PCI performed today can change rapidly within hours due to thrombus formation, progressive dissection or other unforeseen complications. Therefore, the FFR measured immediately after a PCI should be interpreted with caution. Also, whereas the ischemic FFR threshold (0.80) in the stable angina has been clearly established, FFR values within the first days, weeks or months after a PCI can change quickly due to the healing process in the coronary artery itself, intimal hyperplasia, thrombus formation, etc. This means that by definition, the FFR after a PCI is more dynamic and that an adequate FFR value immediately after a PCI should be considerably higher than 0.80 to compensate for any intravascular changes that may occur in the short-term.
Therefore, it is not surprising to see FFR values of at least 0.90 in medical literature as indicative of an acceptable PCI result.9,10 Having said that, at the same time we should realize that most post-stent FFR values in earlier studies were obtained in patients with focal stenosis and without much diffuse disease. It is plausible to think that if diffuse disease is present inside a coronary artery, FFR values ≥ 0.90 will probably not be achieved by just stenting a focal stenosis.
Most likely, in such cases, hyperemic pressure pullback recording (whether motorized or not) or a sophisticated variety called hyperemic pressure pullback gradient will better qualify the functional result after stenting. They will also reveal if the remaining gradients inside the coronary artery are due to insufficient stent deployment or more diffuse disease.11
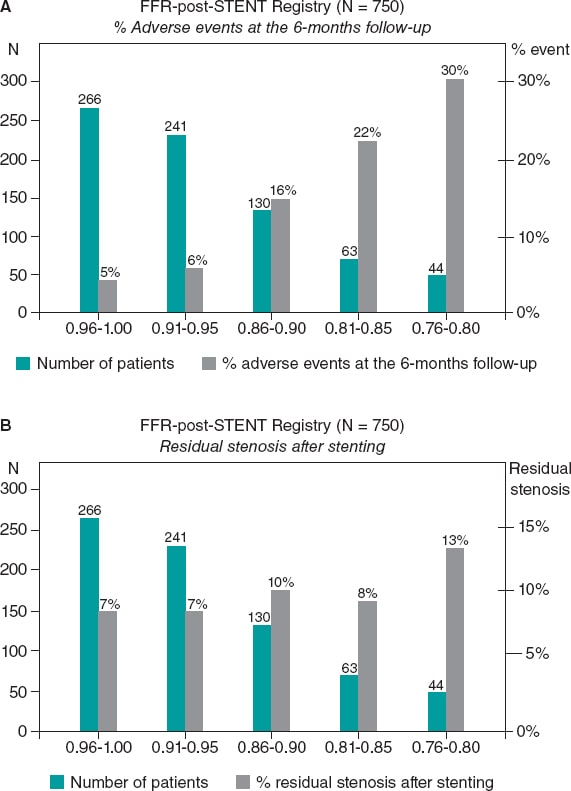
Despite these limitations, the existence of a clear correlation between the FFR values measured immediately after PCI and long-term outcomes is undeniable. This was first described in the FFR-post-STENT Registry of 750 patients that revealed the existence of an inverse correlation between the FFR values measured immediately after the PCI and the rate of restenosis at the 6-month follow-up (figure 1). Such an inverse correlation between high FFR values post-stenting and the mid-term risk of restenosis has been confirmed ever since.12 Still, it is not completely clear if suboptimal FFR values after stenting are due to a focal problem in the stented segment or to diffuse disease elsewhere in the artery. Hyperemic pressure pullback recording and pressure pullback gradient recording have proven that a considerable pressure gradient across the stent is often associated with inappropriate deployments as seen on intravascular ultrasounds or optical coherence tomographies.
Figure 1. Superiority of functional testing compared to angiography alone to predict the outcomes after stenting. A: correlation between post-stenting fractional flow reserve (FFR) and the rate of adverse events at the 6-month follow-up in 750 patients from the FFR-Post-Stent registry. B: correlation between post-stenting angiography and the rate of adverse events at the 6-month follow-up. Reproduced with permission from Pijls et al.9
PATIENT AND VESSEL RELATED PREDICTORS OF POST-PROCEDURAL FFR
At this point, the study conducted by van Zandvoort et al. and recently published on REC: Interventional Cardiology comes into perspective.10 In this study, a large registry of 1000 consecutive patients from 1 large volume cardiac center, the FFR was consistently measured after an angiographically successful PCI without the intention of performing any additional procedures in cases of unexpectedly low FFR values. The authors should be praised for their adherence to this protocol. Afterwards, independent patient and vessel related characteristics were determined as associated with the post-procedural FFR values. Considering that in this study no information was available on the outcomes and that the relationships were not causal per se but associative, a few important lessons can be learned.
In the first place, a very strong predictor of lower FFR values was stent implantation in the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD). In truly normal LADs, the FFR is not different from other arteries and is very close to 1.00.13 However, even in cases of mild disease, the FFR values measured in the LAD are often more damaged compared to other arteries. This is explained by the fact that the LAD perfusion territory is large. One of the major advantages of FFR with respect to other methodologies that only address a coronary artery injury is that the FFR does not only measure the stenosis itself, but also the extent of the perfusion territory. If a similar stenosis (with similar angiographic, intravascular ultrasound or optical coherence tomography characteristics) is located in a coronary artery with a larger perfusion territory, the FFR will be lower. In this regard, the FFR is actually the link between stenosis severity, coronary blood flow, extent of the myocardial perfusion territory, and myocardial ischemia.14 As such, it is plausible that after a successful PCI, the FFR of the LAD will be somehow lower compared to other coronary arteries.
A second interesting observation is that in women, the FFR measured after apparently successful stenting was often higher compared to the males. Van Zandvoort et al. suggest that this might be due to the fact that in women, microvascular disease plays a more predominant role compared to men. Also, that the generation of a hyperemic gradient within the epicardial coronary artery may be blunted by the presence of microvascular disease.10 To confirm that position, more detailed studies of coronary microvasculature are needed. For many years, the assessment of microvascular disease in a true quantitative way has been too hard to pin down. However, recently developed methodology has changed that as follows.15
SIMULTANEOUS ASSESSMENT OF EPICARDIAL AND MICROVASCULAR DISEASE
Recently, the technique for measuring absolute coronary blood flow and microvascular resistance has been introduced as an adjunctive to FFR measurement. This technique is based on the continuous infusion of a saline solution at a low rate and thermodilution. The technique is simple, elegant, accurate, and operator independent.15
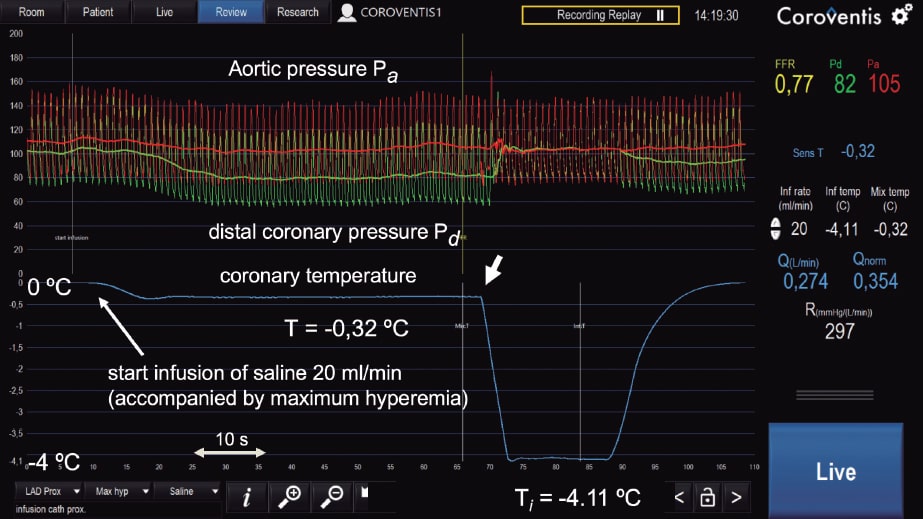
In short, immediately after measuring the FFR, a specifically designed infusion catheter (Rayflow, Hexacath, Paris) is advanced while mounted on the pressure guidewire and placed inside the stent (to study the microvascular resistance of the territory distal to the stent). Then, the infusion of a saline solution at a low rate is started and the absolute coronary blood flow in mL/min is measured in the area of interest using this equation:
Q = Qi × T/Ti × 1.08
where Q is blood flow in the myocardial territory distal to the stent, Qi is the infusion rate of the saline solution (mL/min), Ti is the temperature of the infused saline solution (°C), and T is the temperature in the distal coronary artery after mixing blood and the saline solution. T and Ti are expressed as the difference with respect to body temperature.
With infusion rates = 8 to 10 mL/min, resting blood flow values are obtained and with infusion rates = 20 mL/min, maximum hyperemic values are obtained since the saline solution itself at that rate induces maximum hyperemia in a matter of seconds (figure 2; unpublished data).
Figure 2. Example of absolute coronary blood flow and microvascular resistance measurement in left anterior descending coronary artery following routine fractional flow reserve measurement. On the figure upper side, aortic pressure (Pa), and distal coronary pressure (Pd) are shown in red and green, respectively. The blue line represents coronary temperature as a difference with respect to body temperature (T = 0). After starting the infusion of 20 mL/min of a saline solution (Qi) at room temperature through a dedicated infusion catheter, maximum hyperemia occurs within seconds. Then, after a complete mix of blood and saline solution, a steady-state distal coronary temperature T of 0.32 oC below body temperature is achieved. After withdrawing the pressure/temperature sensor from the tip of the infusion catheter, the infusion temperature (Ti) measured is 4.11 oC below body temperature. Absolute flow (Q) in the coronary artery is calculated using the equation shown in this article (274 mL/min). Microvascular resistance is simply calculated now by Pd/Q and equals 297 Wood units, which is a normal value for the anterior wall. Since the fractional flow reserve value is also known, the normal reference value of coronary flow can be calculated. All parameters are shown online supported by dedicated software (Coroventis, Sweden).
Immediately after the simultaneous measurement of distal coronary pressure and blood flow values, quantitative microvascular resistance Rµ (Wood units) is estimated. In this same way, epicardial disease (indicated by FFR) and microvascular disease (indicated by Rµ) can be assessed and independently distinguished. The position taken by van Zandvoort et al. suggesting that higher FFR values after PCI are related to a higher microvascular resistance in women could be elegantly validated this way.
WHAT IS THE BEST TECHNIQUE TO MEASURE THE FFR VALUES AFTER A PCI?
In the study conducted by van Zandvoort et al. the FFR values measured after the PCI are only briefly described.10 The authors do not report if hyperemic pressure pullback recordings were performed or other techniques used to assess the entire artery. Also, we should mention that to measure intracoronary pressure, not a single true pressure guidewire was used, but the Navvus system instead (ACIST Medical Systems, Eden Prairie, MN, United States). This system is known to overestimate pressure gradients and underestimate FFR mildly in cases of minimal disease or moderately in cases of more severe disease.16 Also, this system is not validated against regular pressure guidewires in post-PCI vessels.
Nevertheless, the measurements were taken meticulously using IV adenosine at a rate of 140 µg/kg/min, giving the opportunity of an easy and reliable estimation of the FFR under stable conditions. We should mention that only 2 out of 1000 patients showed adenosine intolerance, meaning that the infusion of adenosine had to be interrupted due to harmless adenosine-induced, angina-like chest pain. This underlines the safety profile of IV adenosine infusions as seen in tens of thousands of patients in a myriad of other studies.
In future studies on the meaning and interpretation of post-PCI FFR, it would be adviseable to perform hyperemic pressure pullback recordings as outlined in the first part of this article or use the even more sophisticated technique for whole vessel evaluation after PCI recently introduced by Collet et al. and called hyperemic pressure pullback gradient.11 Obviously, all pressure analyses performed inside the stented coronary artery should preferably be performed at maximum hyperemia since gradients at rest inside the artery are 2 to 3 times smaller. Consequently, the signal-to-noise ratio of a resting pullback recording is 2 to 3 times less sensitive.
In conclusion, although outcome data were not presented which, by the way, was not the objective of the study, the interesting trial conducted by van Zandvoort et al.10 teches us about several interesting patient and vessel related predictors of post-procedural FFR measurement. Also, it anticipates the need for future physiological studies to unravel the different factors involved using new research methods on coronary circulation like hyperemic pressure pullback gradients and truly quantitative microvascular resistance (Rµ) measurements.
FUNDING
No funding whatsoever with regards to this article.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
N.H.J. Pijls has received institutional research grants from Abbott and Hexacath. Also, he is a consultant for Abbott, Opsens, and General Electric, and a minor stockholder of Philips, GE, ASML, and Heartflow. L.X. van Nunen declared no conflicts of interest whatsoever.
REFERENCES
1. Pijls NH, van Son JA, Kirkeeide RL, De Bruyne B, Gould KL. Experimental basis of determining maximum coronary, myocardial, and collateral blood flow by pressure measurements for assessing functional stenosis severity before and after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Circulation. 1993;87:1354-1367.
2. Pijls NH, De Bruyne B, Peels K, et al. Measurement of fractional flow reserve to assess the functional severity of coronary-artery stenoses. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:1703-1708.
3. Tonino PA, De Bruyne B, Pijls NH, et al. Fractional flow reserve versus angiography for guiding percutaneous coronary intervention. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:213-224.
4. Gould KL, Lipscomb K, Hamilton GW. Physiologic basis for assessing critical coronary stenosis. Instantaneous flow response and regional distribution during coronary hyperemia as measures of coronary flow reserve. Am J Cardiol. 1974;33:87-94.
5. De Bruyne B, Fearon WF, Pijls NH, et al. Fractional flow reserve-guided PCI for stable coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1208-1217.
6. Zimmermann FM, Omerovic E, Fournier S, et al. Fractional flow reserve-guided percutaneous coronary intervention vs. medical therapy for patients with stable coronary lesions:meta-analysis of individual patient data. Eur Heart J. 2019;40:180-186.
7. Knuuti J, Wijns W, Saraste A, et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:407-477.
8. Patel MR, Calhoon JH, Dehmer GJ, et al. ACC/AATS/AHA/ASE/ASNC/SCAI/SCCT/STS 2017 Appropriate Use Criteria for Coronary Revascularization in Patients With Stable Ischemic Heart Disease:A Report of the American College of Cardiology Appropriate Use Criteria Task Force, American Association for T. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;69:2212-2241.
9. Pijls NH, Klauss V, Siebert U, et al. Coronary Pressure Measurement After Stenting Predicts Adverse Events at Follow-Up. Circulation. 2002;105:2950-2954.
10. van Zandvoort LJC, Masdjedi K, Neleman T, et al. Predictors of postprocedural fractional flow reserve:insights from the FFR-SEARCH study. REC Interv Cardiol. 2020. 2021;3:91-97.
11. Collet C, Sonck J, Vandeloo B, et al. Measurement of Hyperemic Pullback Pressure Gradients to Characterize Patterns of Coronary Atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:1772-1784.
12. Rimac G, Fearon WF, De Bruyne B, et al. Clinical value of post-percutaneous coronary intervention fractional flow reserve value:A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am Heart J. 2017;183:1-9.
13. Pijls NH, Van Gelder B, Van der Voort P, et al. Fractional flow reserve. A useful index to evaluate the influence of an epicardial coronary stenosis on myocardial blood flow. Circulation. 1995;92:3183-3193.
14. De Bruyne B, Hersbach F, Pijls NH, et al. Abnormal epicardial coronary resistance in patients with diffuse atherosclerosis but 'Normal'coronary angiography. Circulation. 2001;104:2401-2406.
15. Xaplanteris P, Fournier S, Keulards DC, et al. Catheter-Based Measurements of Absolute Coronary Blood Flow and Microvascular Resistance:Feasibility, Safety, and Reproducibility in Humans. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;11:e006194.
16. Wijntjens GW, van de Hoef TP, Kraak RP, et al. The IMPACT Study (Influence of Sensor-Equipped Microcatheters on Coronary Hemodynamics and the Accuracy of Physiological Indices of Functional Stenosis Severity). Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;9:e004645.
- Virtual vs face-to-face meetings. Can both of them coexist?
- Translational research in the new era of percutaneous mitral valve interventions
- Elderly patients with comorbidities and acute coronary syndrome: primum non nocere?
- Use of cangrelor in percutaneous coronary interventions: a “new” weapon in the antithrombotic therapeutic armamentarium
Subcategories
Special articles
Original articles
Editorials
Original articles
Editorials
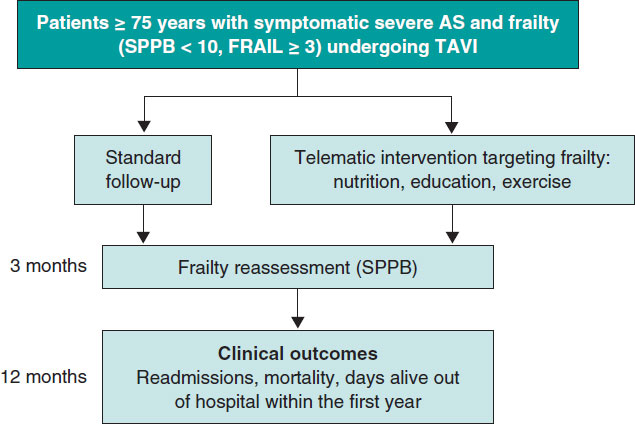
Post-TAVI management of frail patients: outcomes beyond implantation
Unidad de Hemodinámica y Cardiología Intervencionista, Servicio de Cardiología, Hospital General Universitario de Elche, Elche, Alicante, Spain
Original articles
Debate
Debate: Does the distal radial approach offer added value over the conventional radial approach?
Yes, it does
Servicio de Cardiología, Hospital Universitario Sant Joan d’Alacant, Alicante, Spain
No, it does not
Unidad de Cardiología Intervencionista, Servicio de Cardiología, Hospital Universitario Galdakao, Galdakao, Vizcaya, España