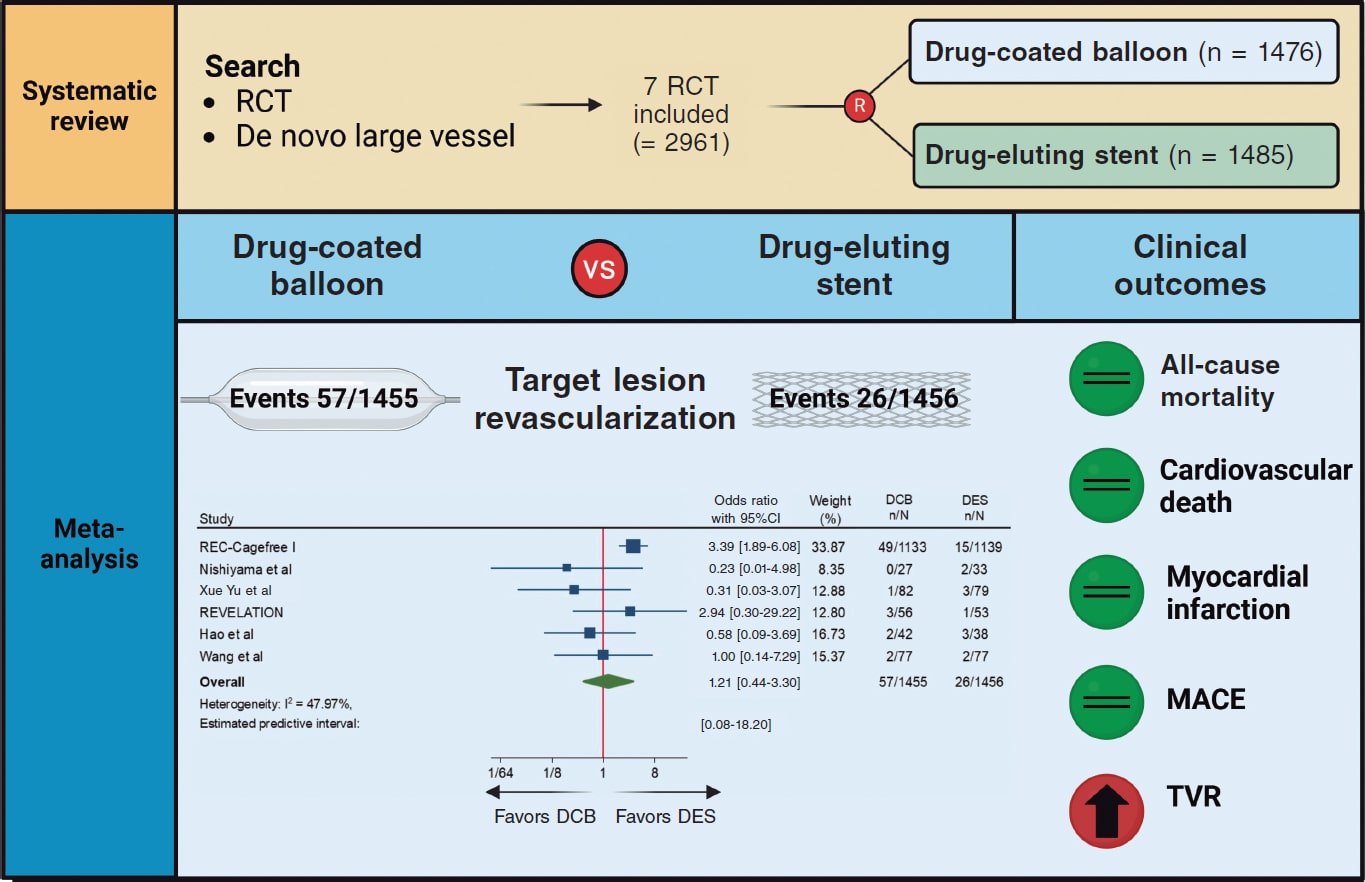
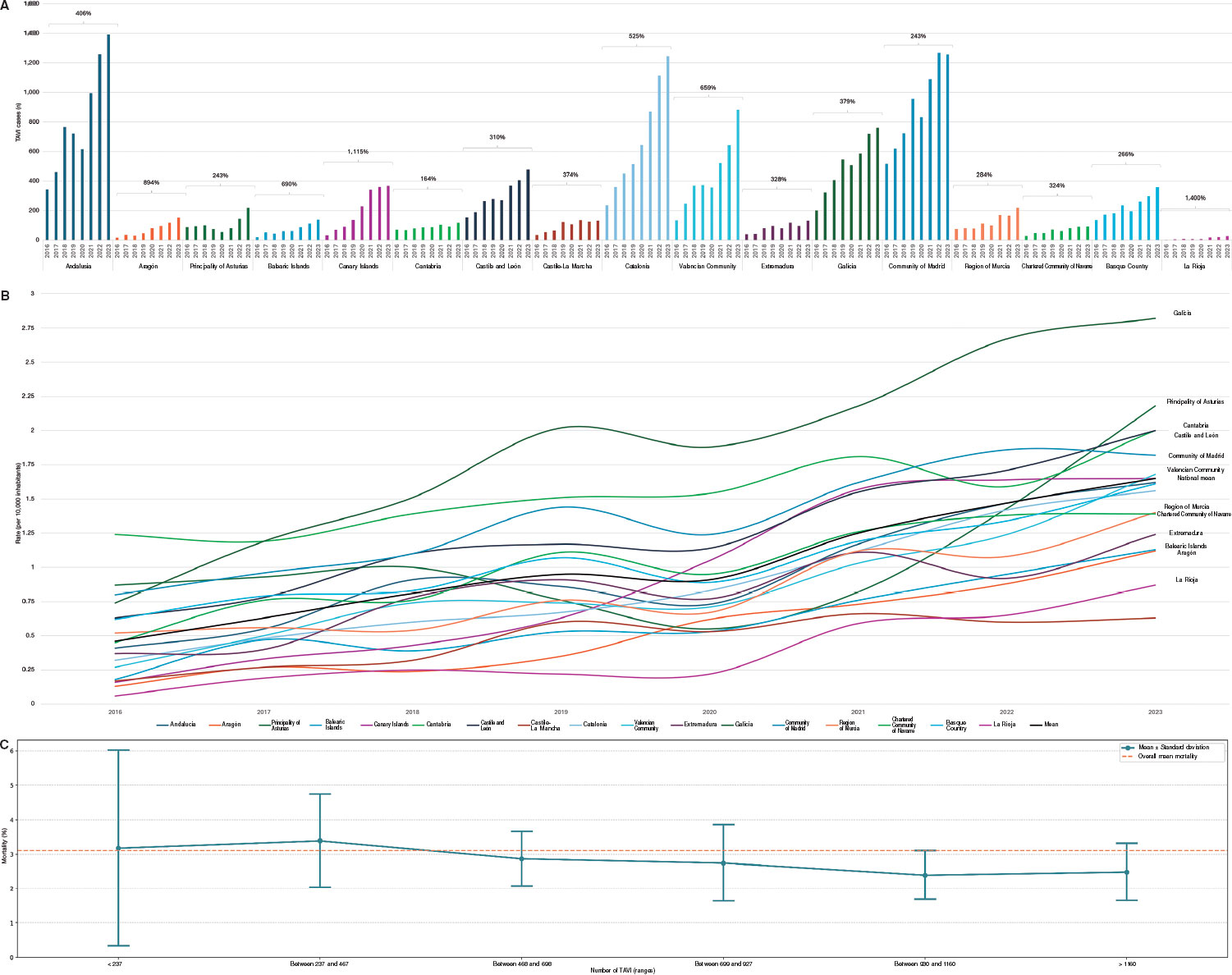
A 12-hour-old neonate, with no relevant prenatal history, presented with an episode of irritability, peripheral hypoperfusion, and metabolic acidosis.
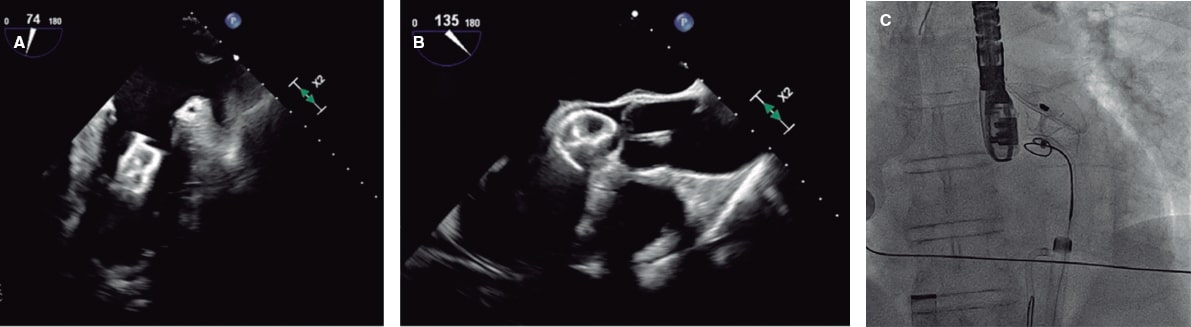
Given the suspicion of sepsis, empirical antibiotic therapy was initiated. The electrocardiogram revealed a QS pattern in leads I and aVL (figure 1), and the lab test results showed a significant elevation of troponins. Echocardiography demonstrated severe biventricular dysfunction with more pronounced hypokinesia in the left ventricular anterolateral region (video S1 and video S2), without visualization of the course of the left coronary artery.
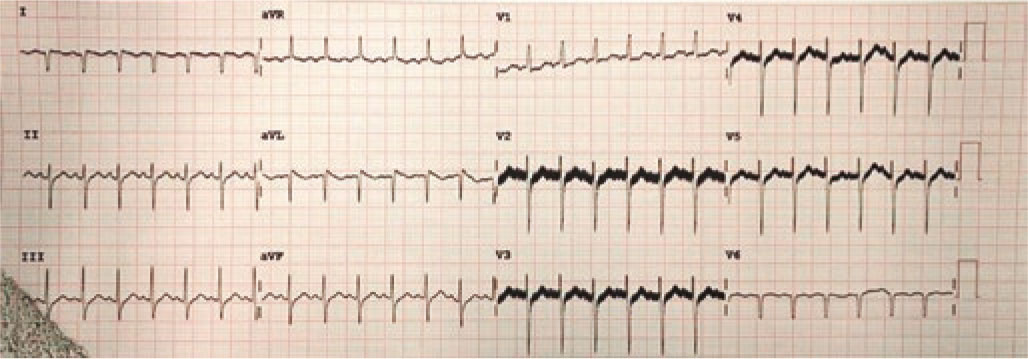
Figure 1.
Due to hemodynamic instability despite intubation and vasoactive support, we performed cannulation for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and cardiac catheterization to rule out coronary artery disease. A normal origin of the left coronary artery was found, with lack of contrast opacification at the junction of the left anterior descending (LAD) and left circumflex (LCX) coronary arteries, and slow distal filling of both vessels (figure 2A and video S3 and video S4; LMCA, left main coronary artery). We performed local fibrinolysis using a microcatheter with administration of 2 boluses of alteplase (0.8 mg and 0.4 mg), achieving recanalization of the LCX and the origin of the LAD (figure 2B).
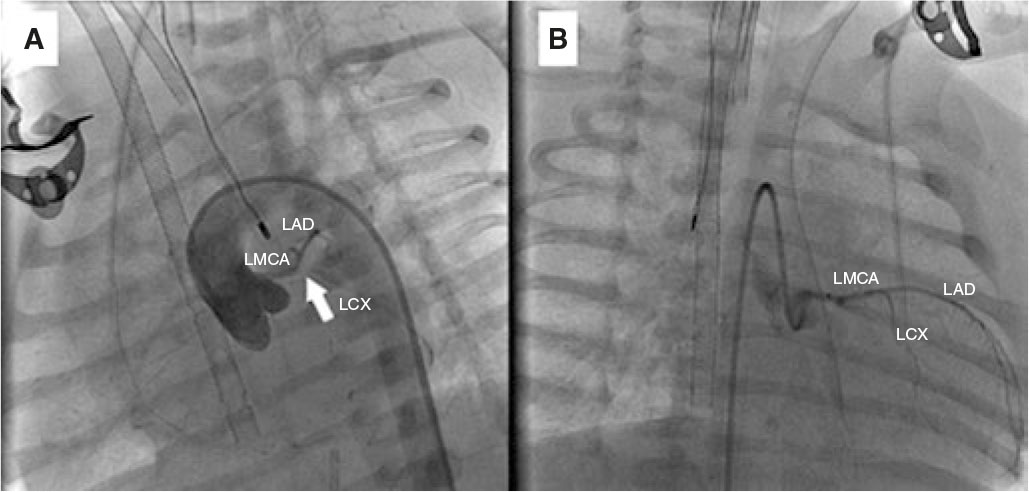
Figure 2.
We performed a second cardiac catheterization at 72 hours after a failed extubation attempt that confirmed adequate coronary flow (video S5). The favorable clinical course allowed weaning from extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and discharge at 44 days of life, with treatment for chronic heart failure (table 1S) and progressive functional recovery (video S6 and video S7).
Although the incidence rate of neonatal acute myocardial infarction is extremely low, its high mortality rate underscores the importance of early diagnosis and prompt treatment.
FUNDING
None declared.
ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS
The patient’s parents gave their informed consent for publication of this case. As this is a single-patient case report, approval by an ethics committee and consideration of SAGER guidelines were deemed unnecessary.
STATEMENT ON THE USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
No artificial intelligence tools were used in the preparation of this manuscript.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTIONS
C. Santos Lorente, A. Mendoza Soto, M. Flores Fernández, L. Albert de la Torre, and D. Herrera Linde were directly involved in the drafting of this article and have read and approved its final version for publication.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
None declared.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Vídeo 1. Santos Lorente C. DOI: 10.24875/RECICE.M25000563
Vídeo 2. Santos Lorente C. DOI: 10.24875/RECICE.M25000563
Vídeo 3. Santos Lorente C. DOI: 10.24875/RECICE.M25000563
Vídeo 4. Santos Lorente C. DOI: 10.24875/RECICE.M25000563
Vídeo 5. Santos Lorente C. DOI: 10.24875/RECICE.M25000563
Vídeo 6. Santos Lorente C. DOI: 10.24875/RECICE.M25000563
Vídeo 7. Santos Lorente C. DOI: 10.24875/RECICE.M25000563