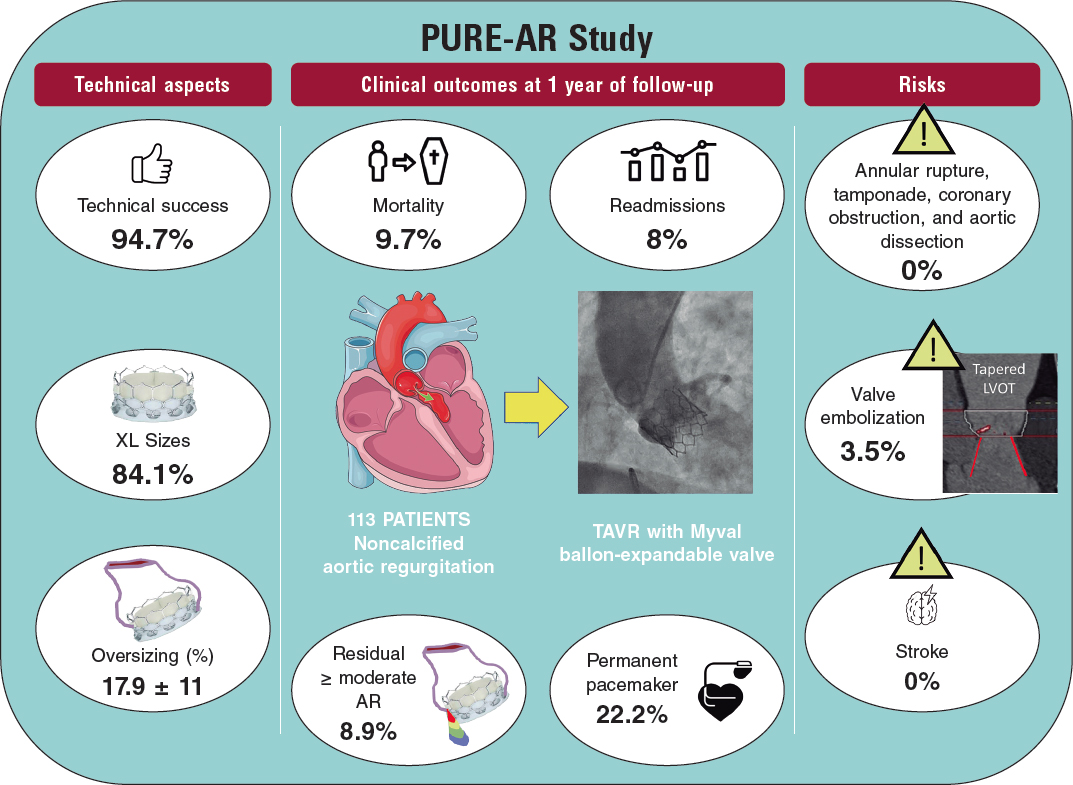
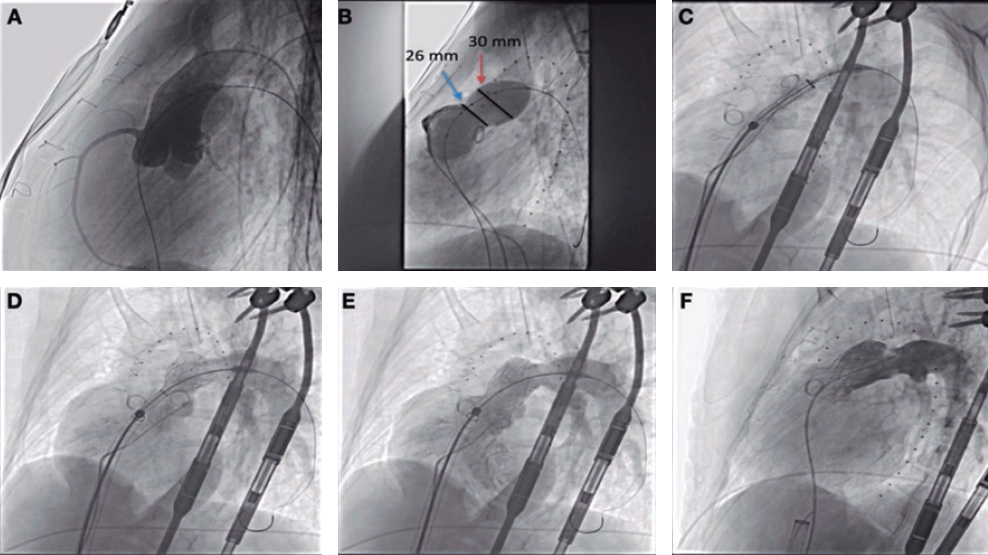
We present the case of a 19-year-old woman with DiGeorge syndrome associated with psychomotor retardation, tetralogy of Fallot, and right pulmonary artery agenesis, treated with right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) transannular patch augmentation during childhood, with severe pulmonary regurgitation and progressive right ventricular enlargement. As a result, pulmonary valve replacement was indicated. Cardiac computed tomography (CT) revealed the presence of severe scoliosis, right sternal deviation, and an elongated RVOT with a minimum diameter of 26 mm at the annular level and 30 mm at the supravalvular level (figure 1A-D, arrows). Because of the clinical and biomechanical characteristics, the anatomy of the RVOT, and the presence of a single pulmonary artery, we performed transcatheter implantation of a self-expanding bioprosthetic Venus valve (Medtech, China). Other valves suitable for large-caliber RVOTs, such as the Myval (Meril, India) have not been granted CE marking for pulmonary implantation.
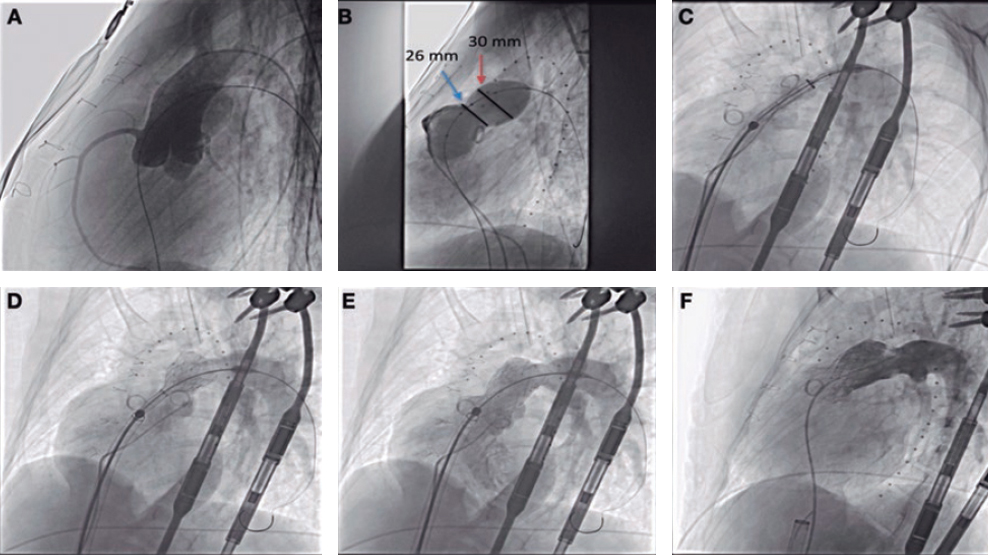
Figure 1.
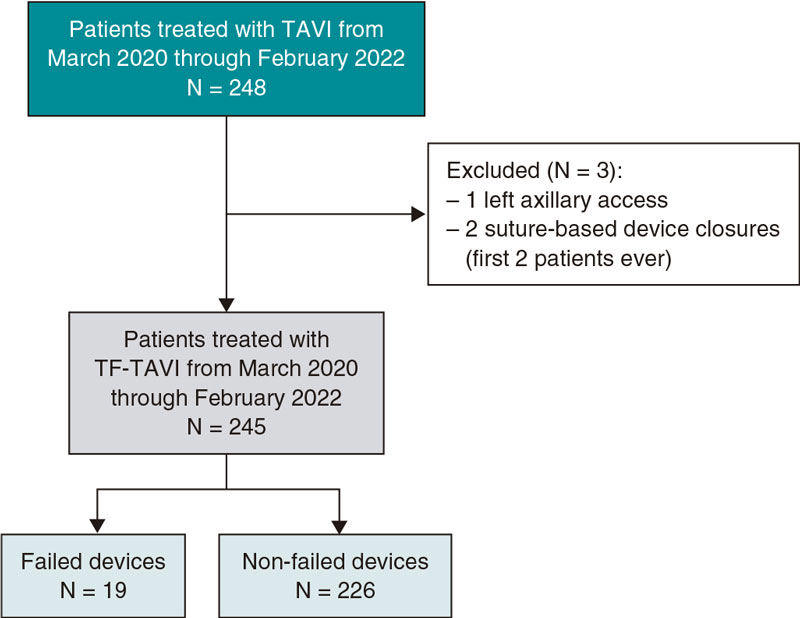
Prior to implantation, the RVOT was sized, and coronary compression was ruled out after occlusive inflation with a 35-mm PTS-X sizing balloon catheter (NuMED, United States). The measurements obtained were consistent with the CT scan results. Consequently, a 30-mm to 25-mm valve was selected (figure 2A,B). A 24-Fr GORE DrySeal introducer sheath and an extra stiff Lunderquist wire guide (Cook Medical, United States) were used to access the left pulmonary artery and progressively deploy the valve initially from the distal segment at the origin of the pulmonary artery and subsequently the proximal segment. Withdrawal of the introducer sheath revealed optimal apposition to the RVOT (figure 2C-F; videos 1 to 4 of the supplementary data). The patient was discharged from hospital 24 hours later, and the valve has remained fully functional ever since with no signs of residual valvular regurgitation.
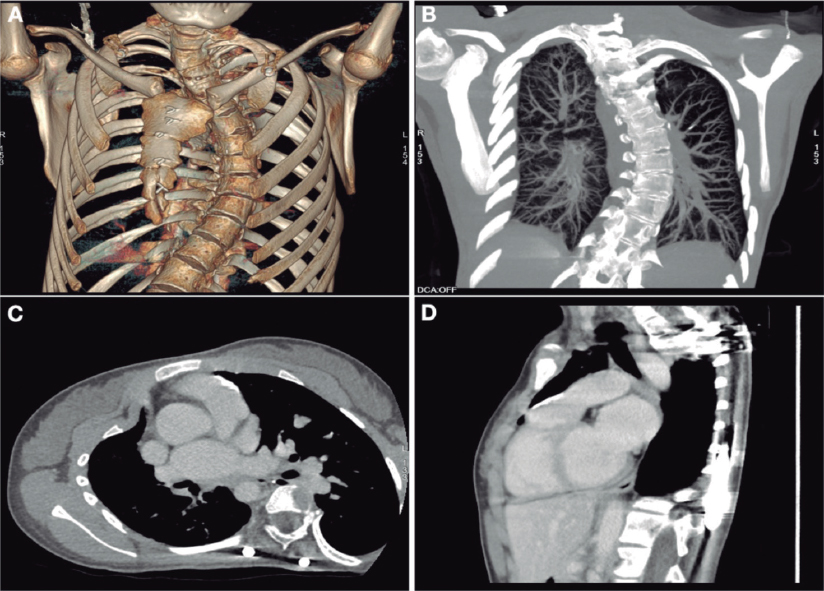
Figure 2.
The patient and her family gave their written informed consent for the publication of this article.
FUNDING
None declared.
ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS
The work has been approved by the ethics committee of our centre. Informed consent was obtained from the patient and family. Our work has not taken into account possible sex and gender variables in accordance with SAGER guidelines.
STATEMENT ON THE USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
No artificial intelligence was used.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTIONS
All the authors contributed equally to this work.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
None declared.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Vídeo 1. Fernández González L. DOI: 10.24875/RECICE.M23000407
Vídeo 2. Fernández González L. DOI: 10.24875/RECICE.M23000407
Vídeo 3. Fernández González L. DOI: 10.24875/RECICE.M23000407
Vídeo 4. Fernández González L. DOI: 10.24875/RECICE.M23000407
* Corresponding author.
E-mail address: luisfg82@hotmail.com (L. Fernández González).